Land Development Techniques
Land development techniques are essential processes that transform raw land into usable spaces for various purposes, such as residential, commercial, or industrial use. These techniques involve a wide range of activities, from clearing and grading to infrastructure development and environmental management. As urban areas continue to expand and rural regions evolve, understanding and implementing effective land development techniques becomes increasingly crucial.
The field of land development is constantly evolving, with new technologies and methodologies emerging to address challenges such as environmental sustainability, urban sprawl, and resource management. This comprehensive guide will explore various aspects of land development techniques, providing valuable insights for developers, urban planners, and environmental professionals.
Key aspects of land development techniques include:
- Site analysis and planning
- Land clearing and preparation
- Infrastructure development
- Environmental impact assessment
- Sustainable design principles
- Urban runoff management
- Topography considerations
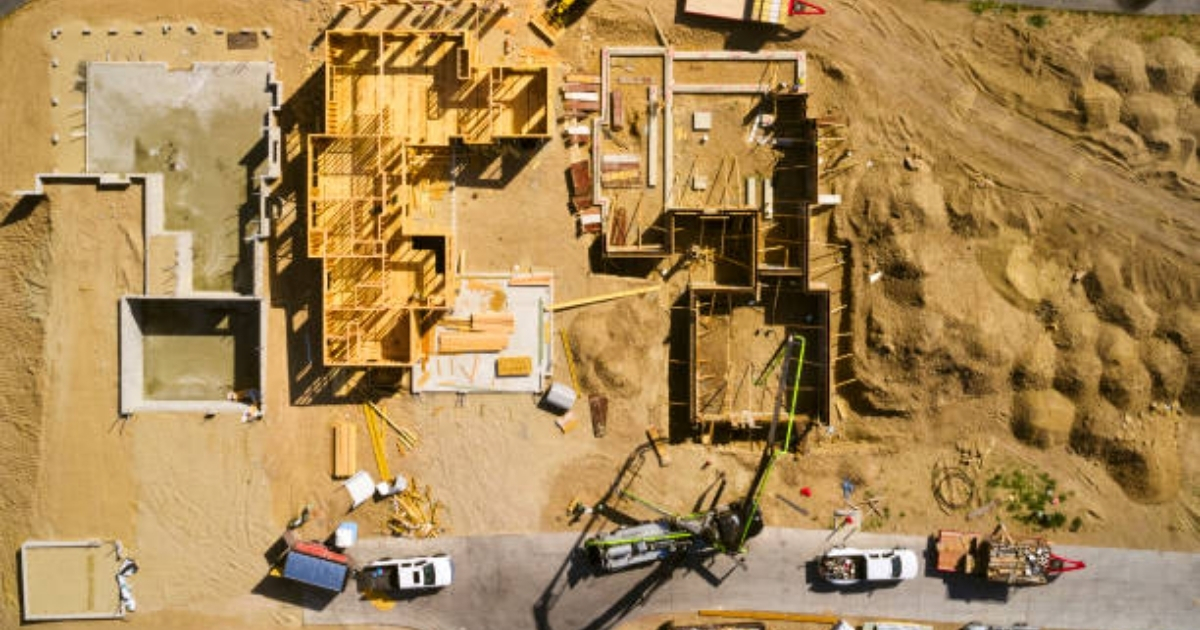
Essential Land Clearing Operations
Land clearing is often the first step in any development project, preparing the site for construction and other activities. This process involves removing vegetation, rocks, and other obstacles to create a clean slate for development.
Vegetation Disposal Methods
Proper vegetation disposal is crucial for efficient land clearing. Methods may include:
- Mulching: Converting vegetation into mulch for landscaping or erosion control
- Burning: Controlled burning of cleared vegetation (subject to local regulations)
- Hauling: Removing vegetation off-site for disposal or recycling
Power Requirements for Clearing Machines
The power needed for clearing operations depends on the size of the project and the type of vegetation. Common equipment includes:
- Bulldozers: For heavy-duty clearing of large areas
- Excavators: For precision clearing and root removal
- Skid steers: For smaller-scale clearing and maneuvering in tight spaces
Mechanical Land Clearing: Pros and Cons
Mechanical land clearing involves using heavy machinery to remove vegetation and prepare the land for development. While efficient, this method has both advantages and drawbacks.
Advantages of Mechanical Clearing
Mechanical clearing offers several benefits:
- Speed: Quickly clears large areas of land
- Efficiency: Reduces labor costs and time requirements
- Versatility: Can handle various types of vegetation and terrain
Disadvantages and Environmental Impacts
However, mechanical clearing also has potential drawbacks:
- Soil compaction: Heavy machinery can compress soil, affecting drainage and plant growth
- Erosion risk: Removing vegetation can increase the likelihood of soil erosion
- Habitat disruption: Can negatively impact local ecosystems and wildlife
Environmental considerations for mechanical clearing:
- Implement erosion control measures
- Preserve buffer zones around water bodies
- Minimize disturbance to sensitive habitats
- Use low-impact equipment when possible
Low Impact Development Strategies
Low Impact Development (LID) strategies aim to minimize the environmental impact of land development by working with natural processes and preserving existing ecosystems.
Innovative Planning Approaches
LID planning approaches focus on:
- Preserving natural drainage patterns
- Minimizing impervious surfaces
- Integrating green infrastructure
Sustainable Design Principles
Key sustainable design principles in LID include:
- Bioretention systems: Using vegetation to filter and absorb stormwater
- Permeable pavements: Allowing water to infiltrate rather than run off
- Green roofs: Incorporating vegetation on building rooftops to reduce runoff and improve insulation
LID techniques offer numerous benefits:
- Improved water quality
- Reduced stormwater runoff
- Enhanced aesthetics and property values
- Increased biodiversity in urban areas
Topography Considerations in Land Development
Topography plays a crucial role in land development, influencing everything from drainage patterns to building placement. Key considerations include:
- Slope analysis: Determining suitable areas for development and identifying potential hazards
- Grading plans: Designing the final contours of the site to manage drainage and create usable spaces
- View corridors: Preserving and enhancing natural vistas and sightlines
Topographic analysis tools:
- Geographic Information Systems (GIS)
- 3D modeling software
- Drone surveys for accurate terrain mapping
Holistic Approach to Site Planning
A holistic approach to site planning considers all aspects of a development project, from environmental impacts to community needs.
Outside-In Design Methodology
The outside-in design methodology focuses on:
- Understanding the site’s context within the larger landscape
- Identifying and preserving natural features and ecosystems
- Integrating the development with existing infrastructure and communities
Space Utilization Strategies
Effective space utilization involves:
- Mixed-use development: Combining residential, commercial, and recreational spaces
- Compact design: Maximizing land use efficiency while preserving open spaces
- Adaptive reuse: Repurposing existing structures to reduce resource consumption
Benefits of holistic site planning:
- Improved environmental sustainability
- Enhanced community integration
- Increased long-term project viability
Creative Ideas in Land Development Projects
Innovation in land development can lead to unique and successful projects. Creative ideas include:
- Vertical forests: Incorporating trees and vegetation into high-rise buildings
- Underground developments: Utilizing subterranean spaces for parking, retail, or transportation hubs
- Floating communities: Developing water-based residential and commercial areas
Factors driving creative land development:
- Urbanization and land scarcity
- Climate change adaptation
- Technological advancements in construction and materials
Market-Driven Flexibility in Development Plans
Successful land development requires adaptability to changing market conditions. Key aspects include:
- Phased development: Allowing for adjustments based on market demand
- Flexible zoning: Accommodating a variety of uses within a single development
- Modular construction: Enabling rapid adaptation to changing needs
Market analysis tools for land development:
- Demographic studies
- Economic forecasting models
- Real estate trend analysis
Team Roles and Responsibilities in Land Development
Effective land development requires a diverse team of professionals working together. Key roles include:
- Urban planners: Developing overall land use strategies
- Civil engineers: Designing infrastructure and managing site grading
- Environmental scientists: Assessing and mitigating ecological impacts
- Architects: Designing buildings and structures
- Landscape architects: Planning outdoor spaces and vegetation
Collaboration strategies for land development teams:
- Regular interdisciplinary meetings
- Shared digital platforms for project management
- Clear communication of project goals and constraints
Protecting Scenic Areas During Development
Preserving scenic areas is essential for maintaining the character and appeal of a development. Strategies include:
- View corridor preservation: Maintaining sightlines to natural features or landmarks
- Setback requirements: Establishing buffer zones around scenic areas
- Design guidelines: Ensuring new structures complement the natural landscape
Tools for scenic area protection:
- Visual impact assessments
- 3D visualization software
- Community engagement surveys
Street Design and Layout in Land Development
Street design plays a crucial role in shaping the character and functionality of a development. Key considerations include:
- Traffic flow optimization: Designing street networks to minimize congestion
- Pedestrian and bicycle infrastructure: Incorporating sidewalks, bike lanes, and multi-use paths
- Green street design: Integrating stormwater management and vegetation into streetscapes
Street design elements:
- Traffic calming measures
- Street lighting and signage
- On-street parking strategies
Master Engineering Validation Process
The master engineering validation process ensures that all aspects of a development project meet technical and regulatory requirements. Steps include:
- Preliminary design review: Assessing initial plans for feasibility and compliance
- Detailed engineering analysis: Conducting in-depth studies of infrastructure systems
- Regulatory compliance verification: Ensuring all plans meet local, state, and federal regulations
Key components of engineering validation:
- Geotechnical investigations
- Hydraulic and hydrologic modeling
- Structural analysis of proposed buildings and infrastructure
Environmental Impact Assessment in Land Development
Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) is a critical process in land development, evaluating the potential effects of a project on the natural environment.
Key aspects of EIA include:
- Baseline studies: Documenting existing environmental conditions
- Impact prediction: Forecasting potential effects of the development
- Mitigation planning: Developing strategies to minimize negative impacts
EIA methodologies:
- Matrix analysis
- Network diagrams
- Geographic Information Systems (GIS) modeling
Benefits of thorough EIA:
- Improved project sustainability
- Reduced legal and regulatory risks
- Enhanced stakeholder engagement and public acceptance
What are the most common land development techniques used today?
The most common land development techniques used today include site analysis, land clearing, grading, and infrastructure development. These fundamental processes form the backbone of most development projects, whether residential, commercial, or industrial. Additionally, sustainable development practices such as Low Impact Development (LID) and green infrastructure are becoming increasingly prevalent as developers seek to minimize environmental impacts and create more resilient communities.
How do land development techniques impact the environment?
Land development techniques can have significant impacts on the environment, both positive and negative. On the negative side, traditional development practices can lead to habitat destruction, increased stormwater runoff, and soil erosion. However, modern sustainable development techniques aim to mitigate these impacts by preserving natural features, implementing green infrastructure, and using environmentally friendly materials. The overall environmental impact depends largely on the specific techniques used and the care taken to implement them responsibly.
What are some innovative land development techniques for sustainable urban planning?
Innovative land development techniques for sustainable urban planning include vertical forests, which integrate trees and vegetation into high-rise buildings, and underground developments that utilize subterranean spaces for various purposes. Other innovative approaches include the implementation of green roofs, permeable pavements, and bioretention systems to manage stormwater and improve urban ecology. Additionally, the concept of “smart cities” incorporates advanced technologies and data-driven decision-making to optimize resource use and improve quality of life in urban areas.
How can land development techniques help manage urban runoff?
Land development techniques can significantly help manage urban runoff through various strategies. Low Impact Development (LID) approaches, such as bioretention systems and permeable pavements, allow stormwater to infiltrate the ground naturally, reducing runoff volume. Detention basins and constructed wetlands can temporarily store and filter stormwater, mitigating flood risks and improving water quality. Green roofs and rainwater harvesting systems can also play a role in reducing runoff from buildings. By incorporating these techniques into development plans, urban areas can better manage stormwater and reduce the strain on traditional drainage infrastructure.
What role does topography play in land development techniques?
Topography plays a crucial role in land development techniques, influencing many aspects of site planning and design. It affects drainage patterns, determining how water will flow across the site and where stormwater management features should be placed. Topography also impacts the placement of buildings, roads, and other infrastructure, with slope considerations affecting construction costs and feasibility. Additionally, topographic features can create opportunities for unique design elements, such as terraced landscapes or buildings that integrate with hillsides. Understanding and working with the existing topography is essential for creating efficient, sustainable, and aesthetically pleasing developments.